
In addition to the above defined elbows there are few more types of elbows which are not used on regular basis. Few of them has been defined below.
A reducing elbow is a type of fitting which is used to join two pipes of different sizes. The reducing elbow is so called because it looks like a reducing piece and elbow combined into one. The reducing elbow eliminates one pipe fitting (reducer) and reduces the welding by more than one-third. Also, the gradual reduction in diameter throughout the arc of the reducing elbow provides lower resistance to flow and reduces the effect of stream turbulence and potential internal erosion. These features prevent sizable pressure drops in the line.
For many suppliers it is a non standard item resulting into high price with a long delivery time. The use of a “normal” elbow with a separate reducer is an option if the situation allows.
Male pipe elbows and female pipe elbows are popular tube fittings which provide an fluid flow directional change of a tubing run. While a male pipe elbow is used to connect fractional tube to female tapered pipe thread, a female elbow is used to connect fractional tube to male NPT thread. These types of tube fittings like male elbows and female elbows have been specifically designed for use on instrumentation, process and control systems and equipment employed in chemical, petroleum, fluid power, electronic and pulp and paper plants.
The weakest point on an elbow is the inside radius. ASME B16.9 only standardizes the center to face dimensions and some “squareness” dimensional tolerances. The wall thickness at the weld line location even is standardized, but not through the rest of an elbow. The standard states that the minimum tolerance will be within 12.5% of the minimum ordered wall thickness of the pipe. A maximum tolerance is specified only at the ends of the fitting. Many providers of butt weld elbows provide one schedule greater thickness so that sufficient wall thickness, after forming, remains.
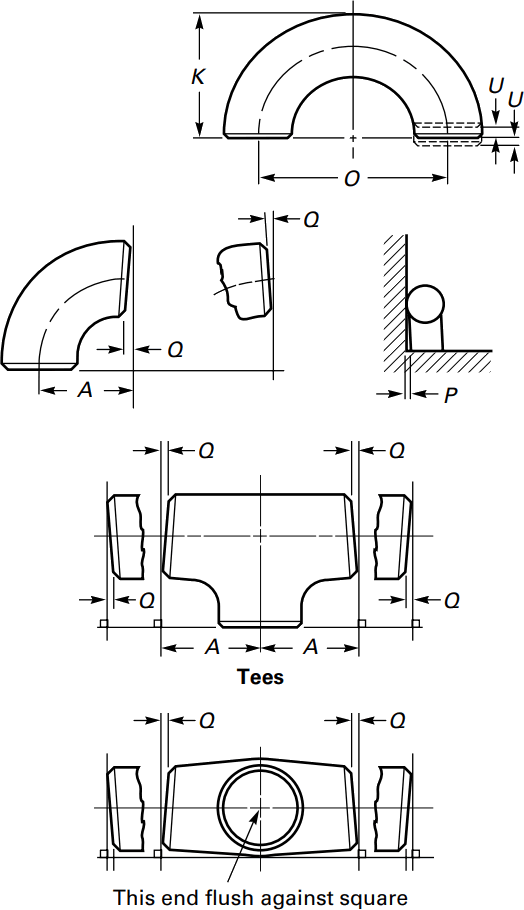
ASME B16.9 Standard covers overall dimensions, tolerances,ratings, testing, and markings for factory-made wrought buttwelding fittings in sizes NPS 1⁄2 through NPS 48 (DN 15 through DN 1200).
Download PDF| Nominal | Outside Diameter | 90° Elbows | 45° Elbows | 180° Returns | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pipe Size | Long Radius | Short Radius | Long Radius | Long Radius | ||||
| (inches) | (mm) | (inches) | Center to Face | Center to Face | Center to Face | Radius | Center to Center | Back to face |
| (inches) | (inches) | (inches) | (inches) | (inches) | (inches) | |||
| 1/2 | 21.3 | 0.84 | 1.5 | – | 5/8 | 2 | 1.875 | |
| 3/4 | 26.7 | 1.05 | 1.125 | – | 7/16 | 2.25 | 1.6875 | |
| 1 | 33.4 | 1.315 | 1.5 | 1 | 7/8 | 3 | 2.1875 | |
| 1.25 | 42.2 | 1.66 | 1.875 | 1.25 | 1 | 3.75 | 2.75 | |
| 1.5 | 48.3 | 1.9 | 2.25 | 1.5 | 1.125 | 3 | 4.5 | 3.25 |
| 2 | 60.3 | 2.375 | 3 | 2 | 1.375 | 4 | 6 | 4.1875 |
| 2.5 | 73 | 2.875 | 3.75 | 2.5 | 1.75 | 5 | 7.5 | 5.1875 |
| 3 | 88.9 | 3.5 | 4.5 | 3 | 2 | 6 | 9 | 6.25 |
| 3.5 | 101.6 | 4 | 5.25 | 3.5 | 2.25 | 7 | 10.5 | 7.25 |
| 4 | 114.3 | 4.5 | 6 | 4 | 2.5 | 8 | 12 | 8.25 |
| 5 | 141.3 | 5.563 | 7.5 | 5 | 3.125 | 10 | 15 | 10.3125 |
| 6 | 168.3 | 6.625 | 9 | 6 | 3.75 | 12 | 18 | 12.3125 |
| 8 | 219.1 | 8.625 | 12 | 8 | 5 | 12 | 24 | 16.3125 |
| 10 | 273.1 | 10.75 | 15 | 10 | 6.25 | 15 | 30 | 20.375 |
| 12 | 323.9 | 12.75 | 18 | 12 | 7.5 | 18 | 36 | 24.375 |
| NOMINAL PIPE SIZE NPS | ANGULARITY TOLERANCES | ANGULARITY TOLERANCES |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Off Angle Q | Off Plane P |
| ½ to 4 | 0.03 | 0.06 |
| 5 to 8 | 0.06 | 0.12 |
| 10 to 12 | 0.09 | 0.19 |
| 14 to 16 | 0.09 | 0.25 |
| 18 to 24 | 0.12 | 0.38 |
| 26 to 30 | 0.19 | 0.38 |
| 32 to 42 | 0.19 | 0.5 |
| 44 to 48 | 0.18 | 0.75 |
All dimensions are given in inches. Tolerances are equal plus and minus except as noted.
The ASME B16.9 pipe fittings can be used under the jurisdiction of the ASME Boiler & Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC) as well as the ASME Code for pressure piping. Referencing pressure ratings of flanges per ASME B16.5, they can be designated as Classes 150, 300, 600, 900, 1500 and 2500. The allowable pressure ratings for ASME B16.9 pipe fittings may be calculated as for straight seamless pipe of equivalent material in accordance with the rules established in the applicable sections of ASME B31 Code for pressure piping.
The design of butt welding pipe fittings made to ASME B16.9 shall be established by one of the following methods: (a) mathematical analyses contained in pressure vessel or piping codes; (b) proof testing; (c) experimental stress analysis with hydrostatic testing to validate experimental results; (d) detailed stress analysis with results evaluation.
Generally, ASME B16.9 pipe fittings shall be marked to show the following details: “trademark + material grade + wall thickness + size + heat number”. For example, “M ASTM A234 WP5 SCH80 6″ 385“. When steel stamps are used, care shall be taken so that
the marking is not deep enough or sharp enough to cause cracks or to reduce the wall thickness of the fitting below the minimum allowed.
The ASME B16.9 fittings may be made from an extensive range of mateirals covering (1) carbon and low-alloy steels in accordance with ASTM A234 and ASTM A420; (2) austenitic and duplex stainless steels in accordance with ASTM A403 and ASTM A815; (3) nickel alloys in accordance with ASTM B366; (4) aluminum alloys in accordance with ASTM B361; and (5) titanium alloys in accordance with ASTM B363.
Sizes 1/2″ – 48″
Pipe fitting dimensions are in either metric or Standard English.
Because pipe fitting covers Pipe Fitting Dimensions several aspects, only the most common pipe fitting sizes can be given here. The most applied version is the 90° long radius and the 45° elbow, while the 90° short radius elbow is applied if there is too little space. The function of a 180° elbow is to change direction of flow through 180°. Both, the LR and the SR types have a center to center dimension double the matching 90° elbows. These fittings will generally be used in furnesses or other heating or cooling units.
Some of the standards that apply to buttwelded fittings are listed below. Many organizations such as ASME, ASTM, ISO, MSS, etc. have very well developed standards and specifications for buttwelded fittings. It is always up to the designer to ensure that they are following the applicable standard and company specification, if available, during the design process.
Some widely used pipe fitting standards are as follows:
对配件进行目视检查,以检查任何表面缺陷。检查管件主体和焊缝是否有任何可见的表面缺陷,例如凹痕、模痕、孔隙、底切等。根据适用标准进行验收。从仓库到您身边,我们既要速度更要靠谱!全程追踪物流、品质护货不马虎,每一次交付都较真 “说到做到”,让客户更快 更满意的拿到心仪货品
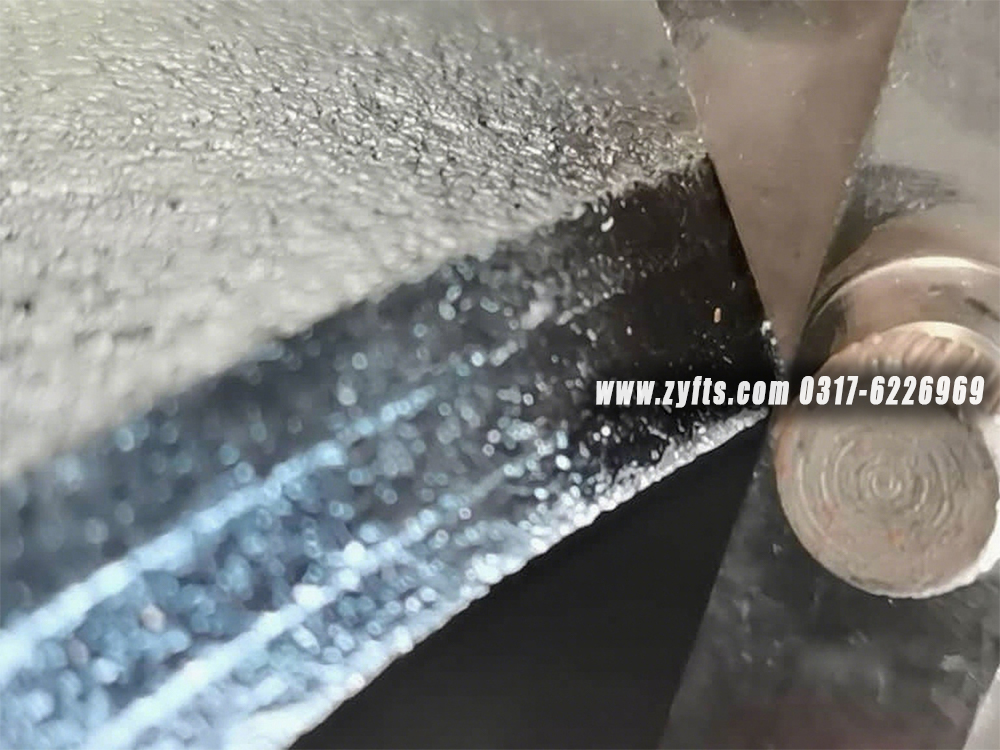
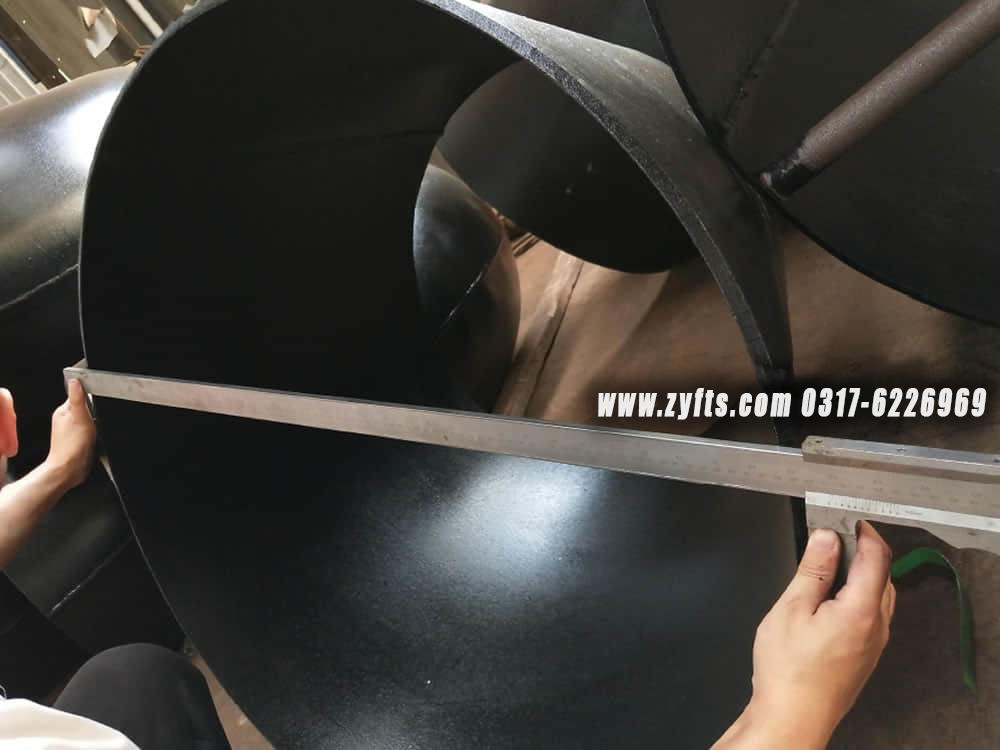
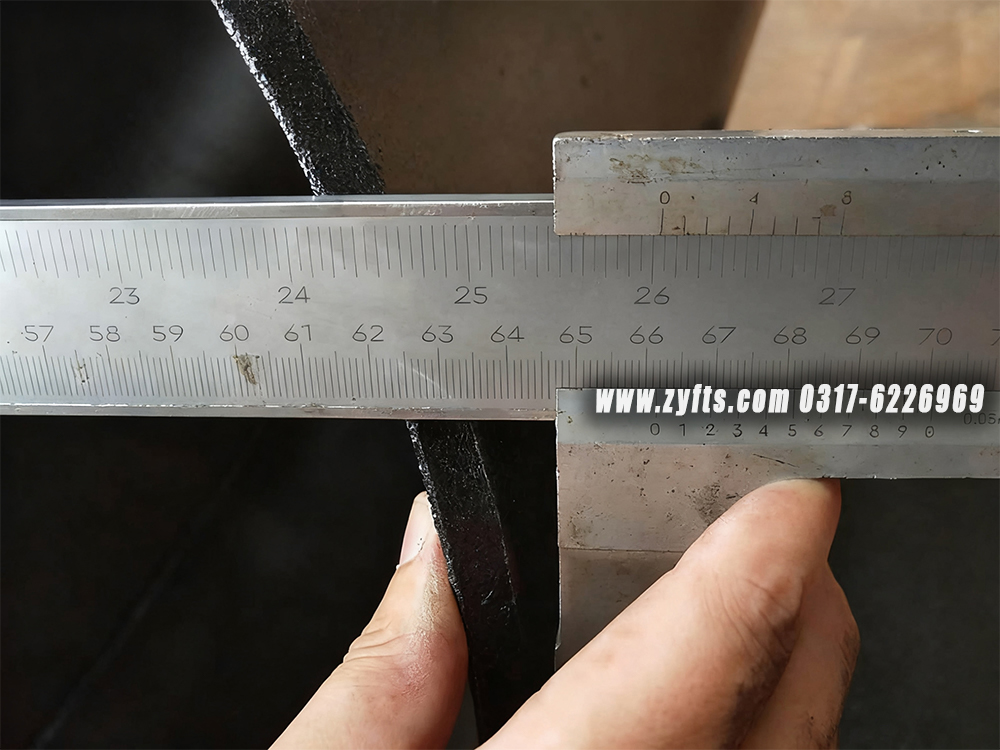









对于带喷漆的碳钢法兰的包装,我们会使用气泡膜来保护喷漆。对于未喷漆或长期运输上油的法兰,我们建议客户使用防锈纸和塑料袋以防止生锈。后期我们会根据客户的要求和实际情况 细致包装 保证客户收到完整的产品
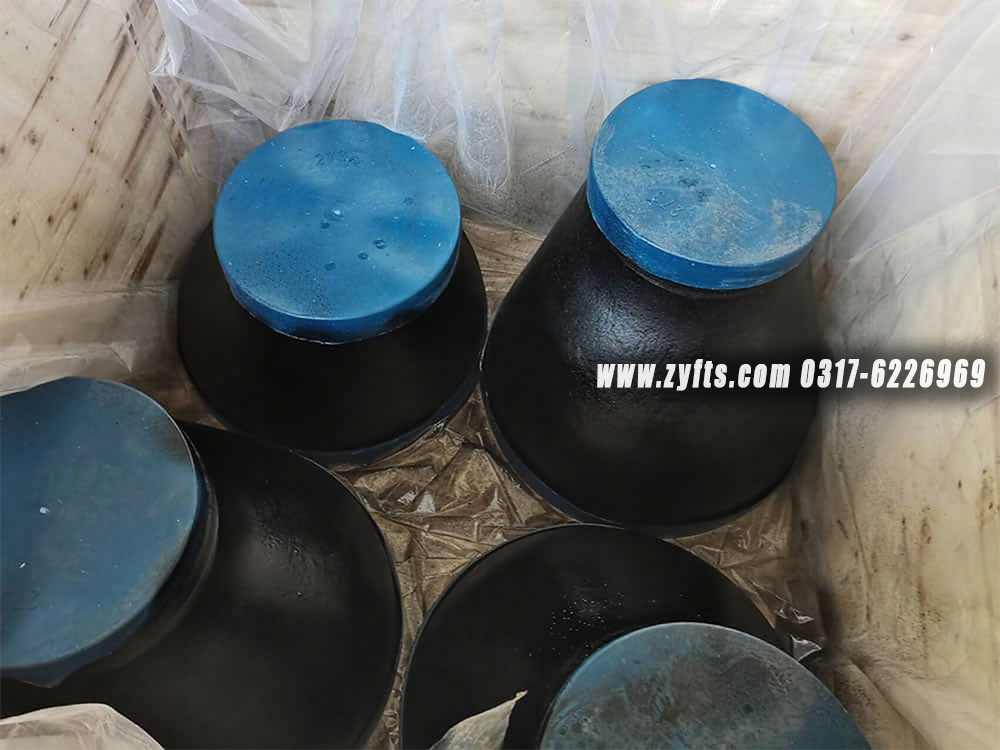
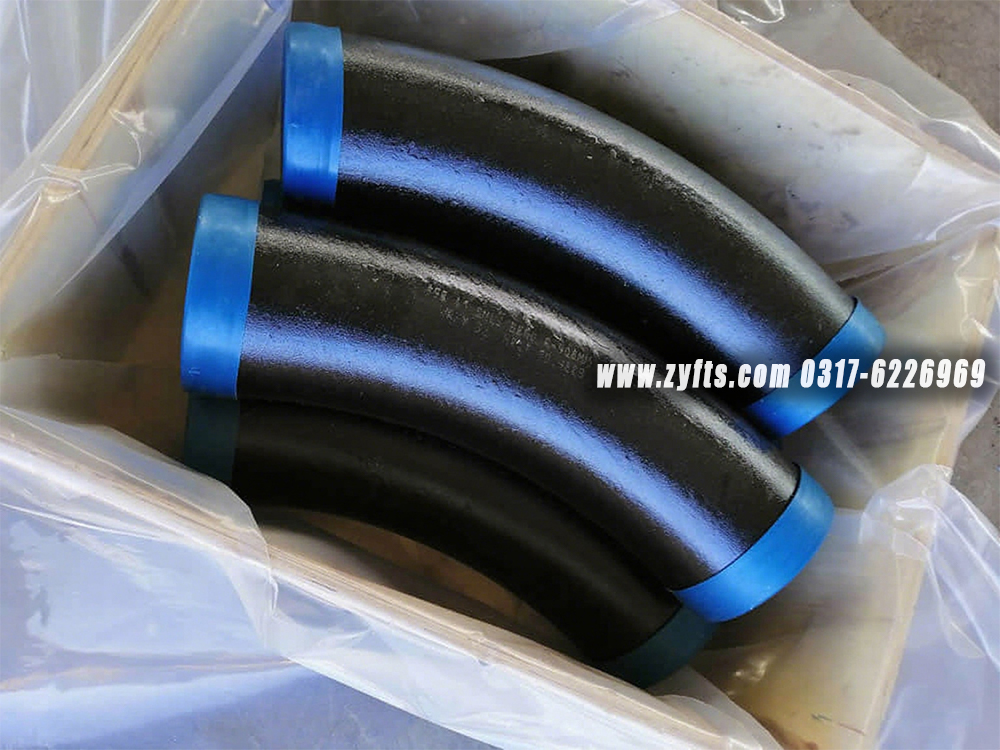







我们的响应式服务确保时效,专业团队精准把握您的需求,以白手套级服务标准为您快速配齐所需材料。
